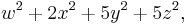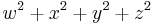15 and 290 theorems
The 15 theorem of John H. Conway and W. A. Schneeberger (Conway–Schneeberger Fifteen Theorem), proved in 1993, states that if an integral quadratic form with integer matrix represents all positive integers up to 15, then it represents all positive integers. (All quadratic forms in this article are implicitly assumed to be positive definite.) The proof was complicated, and was never published. Manjul Bhargava found a much simpler proof which was published in 2000.
This result is the best possible, as there are such forms as, for example,
that represent all positive integers other than 15.
A quadratic form representing all positive integers is sometimes called universal. For example,
is universal because every positive integer can be written as a sum of 4 squares, by Lagrange's four-square theorem. By the 15 theorem, to verify this it is sufficient to check that every positive integer up to 15 is a sum of 4 squares. (This does not give an alternative proof of Lagrange's theorem, because Lagrange's theorem is used in the proof of the 15 theorem.)
A more precise version of the 15 theorem says that if an integral quadratic form with integral matrix represents the numbers 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 14, 15 (sequence A030050 in OEIS) then it represents all positive integers. Moreover, for each of these 9 numbers, there is such a quadratic form representing all positive integers except for this number.
There are two different notions of integrality for integral quadratic forms: it can be called integral if its associated symmetric matrix is integral ("integral matrix"), or if all its coefficients are integral ("integer valued"). For example, x2 + xy + y2 is integer valued but does not have integral matrix.
In 2005 Manjul Bhargava and Jonathan P. Hanke announced a proof of Conway's conjecture that a similar theorem holds for integer valued integral quadratic forms, with the constant 15 replaced by 290. The proof is forthcoming in Inventiones Mathematicae.
A more precise version states that if an integer valued integral quadratic form represents all the numbers 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 10, 13, 14, 15, 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 26, 29, 30, 31, 34, 35, 37, 42, 58, 93, 110, 145, 203, 290 (sequence A030051 in OEIS) then it represents all positive integers, and for each of these 29 numbers there is such a quadratic form representing all positive integers with the exception of this one number.
Bhargava has found analogous criteria for an integral quadratic form to represent all primes (the set {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37, 41, 43, 47, 67, 73} (sequence A154363 in OEIS)) and for such a quadratic form to represent all positive odd integers (the set {1, 3, 5, 7, 11, 15, 33} (sequence A116582 in OEIS)).
References
- Bhargava, Manjul On the Conway–Schneeberger fifteen theorem. Quadratic forms and their applications (Dublin, 1999), 27–37, Contemp. Math., 272, Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, 2000.
- Conway, J. H. Universal quadratic forms and the fifteen theorem. Quadratic forms and their applications (Dublin, 1999), 23–26, Contemp. Math., 272, Amer. Math. Soc., Providence, RI, 2000.
- 290 theorem article
- Universal quadratic forms and the 290-Theorem" resource page